Sparse Non-homogeneous Pooling for Feature Map Fusion of LIDAR and Camera
Contents:
Sparse Non-homogeneous Pooling for Feature Map Fusion of LIDAR and Camera
Introduction
This is the introduction of the extension of the published work Fusing Bird View LIDAR Point Cloud and Front View Camera Image for Deep Object Detection. The code is released on the github Sparse_Pooling. The problem considered here is the feature fusion of different sensors in CNNs shown as the figure below
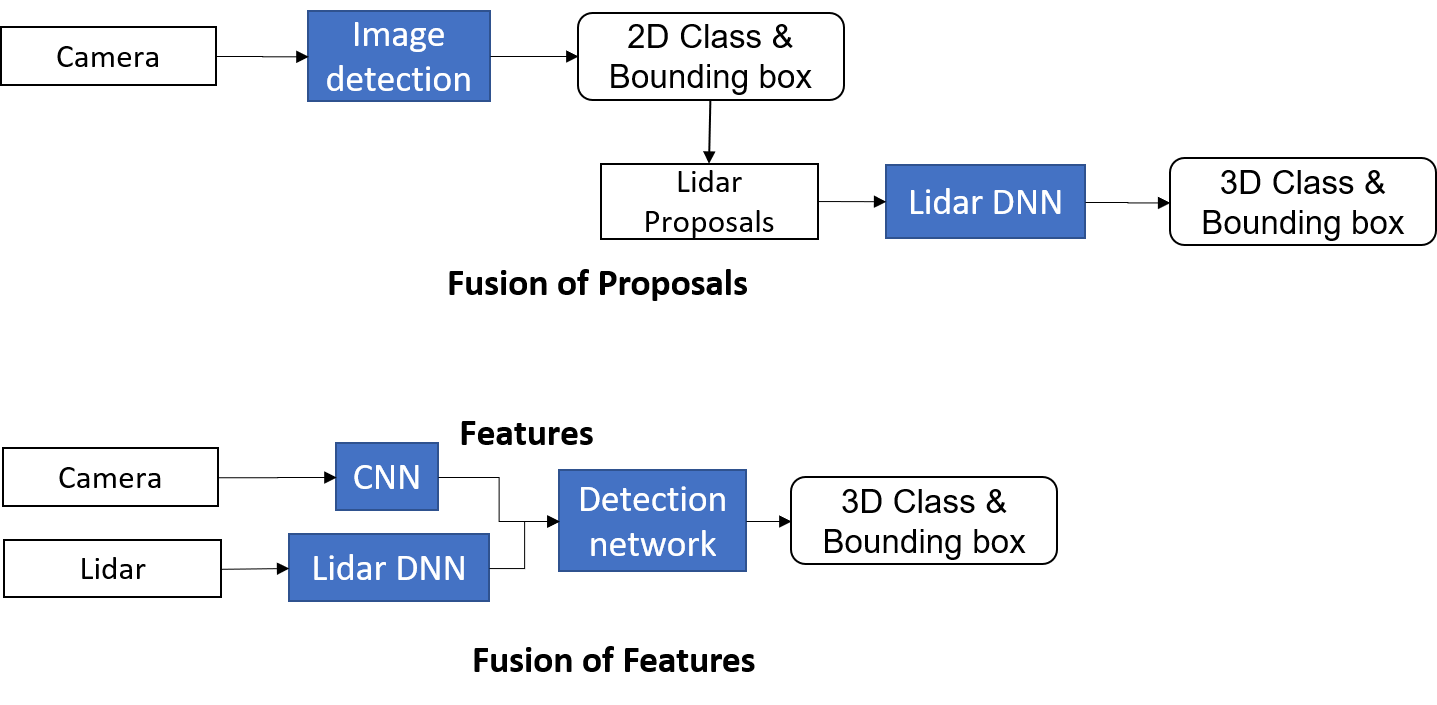
The fusion happens at the middle-stage which is of the best performance according to the Kitti Benchmark on July 23, 2018. The middle-stage fusion propose to fuse features after the convolution and down-sampling operations of the raw data and before the region proposal network (RPN). The fusion keeps the training of the network end-to-end.
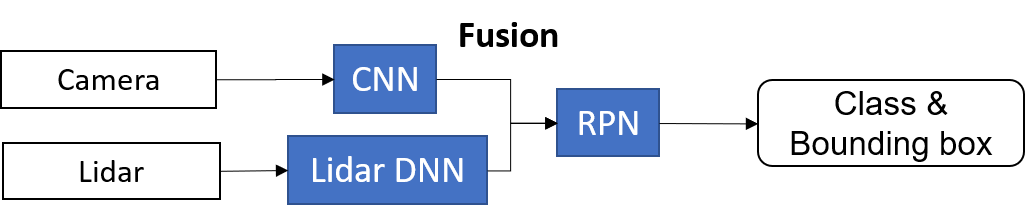
The main contributions of the Sparse Non-homogeneous Pooling Layer (SHPL) are:
Sparse Pooling Transforms and Preserves the Whole feature map
With the feature map preserved while the information of both sensors are fused, not only detection but also semantic segmentation and other tasks with fused features.
One-stage detection framework can be utilized without RoI pooling which improves efficiency.
Easy to Incorperate with Existing Networks and Very Little Overhead
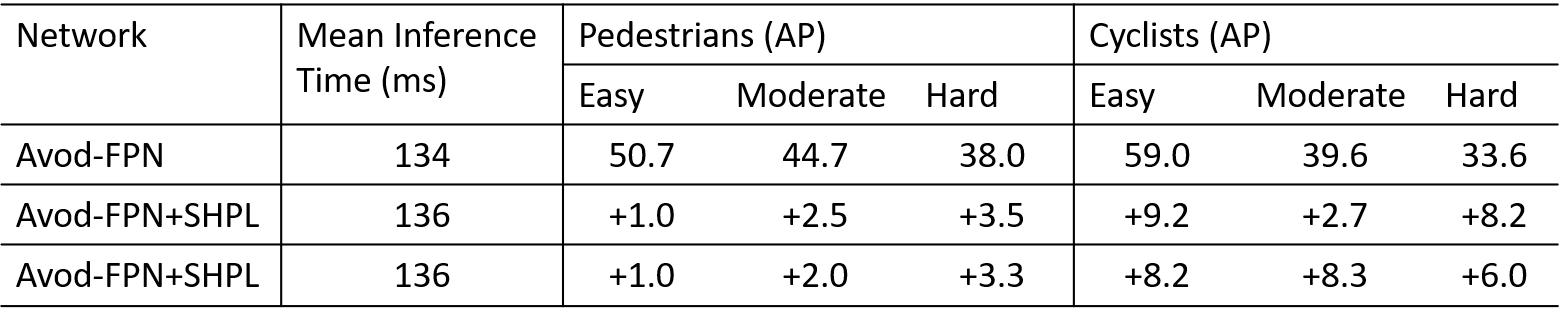
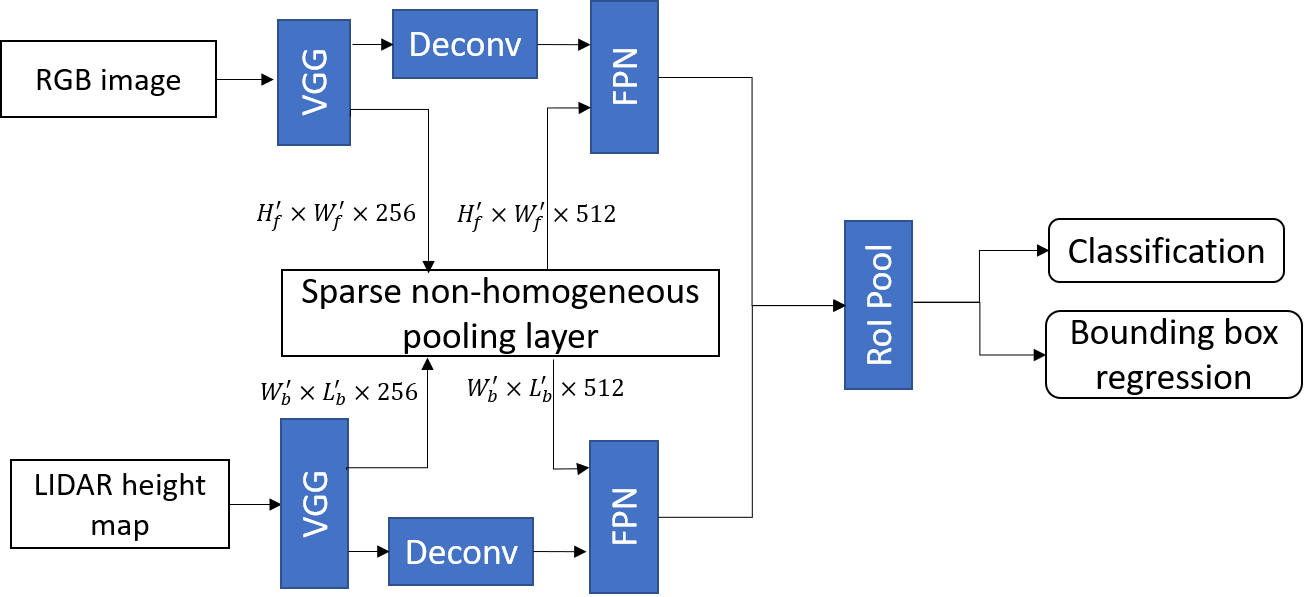
The following figure shows the integration of SHPL with Avod-FPN. It improves the average precision (AP) by feature fusion, adding a subtle overhead to the mean inference time on the validation dataset.
Videos
Researchers
| Zining Wang | Graduate Student | Email Link |
| Wei Zhan | Graduate Student | Email Link |
